Understanding Contract Law: Essential Elements and Legal Implications
Introduction Contract law is a fundamental aspect of the legal system that governs agreements between parties. Whether in business transactions, employment relationships, or personal agreements, contracts play a crucial role in defining rights and obligations. Understanding contract law is essential for individuals and businesses to ensure compliance and protect their interests. This article explores the essential elements of contract law, common types of contracts, and the legal implications of breaches.
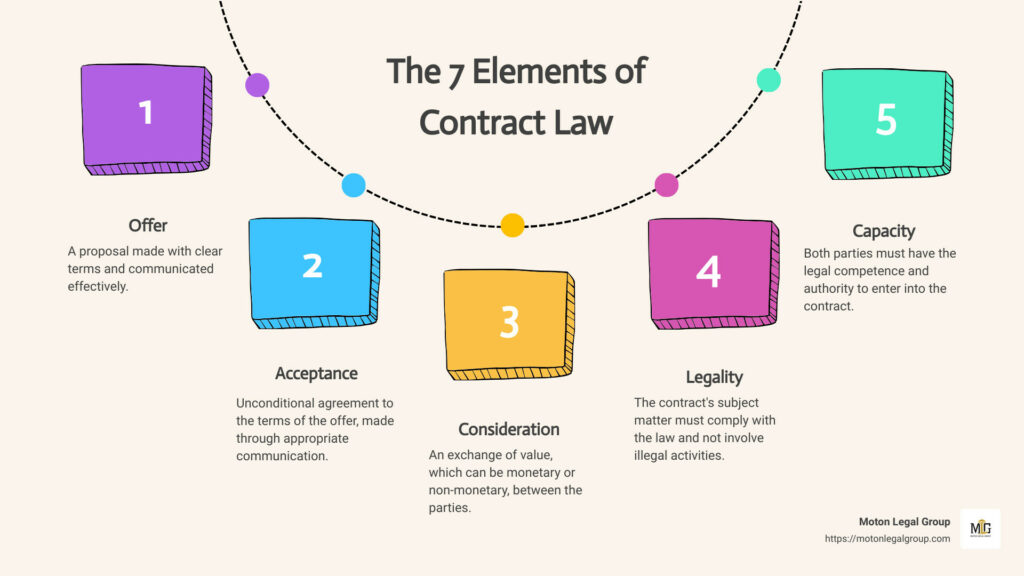
Essential Elements of a Valid Contract For a contract to be legally binding, it must meet specific requirements. The fundamental elements of a valid contract include:
- Offer and Acceptance: One party must make a clear and definite offer, and the other party must accept it unambiguously.
- Consideration: Each party must provide something of value in exchange for the promise or obligation undertaken by the other party.
- Mutual Consent: Both parties must agree to the contract terms willingly and with a clear understanding of their obligations.
- Capacity: The parties entering into the contract must have the legal capacity to do so, meaning they must be of legal age and sound mind.
- Legality: The contract’s purpose must be lawful; agreements involving illegal activities are not enforceable.
Types of Contracts Contracts come in various forms depending on their purpose and legal requirements. Some common types include:
- Express Contracts: These contracts have explicitly stated terms, either written or spoken, that outline the parties’ obligations.
- Implied Contracts: Formed by the parties’ actions rather than written or spoken words, implying an agreement exists.
- Bilateral Contracts: Involve two parties making promises to each other.
- Unilateral Contracts: One party makes a promise in exchange for the other party performing a specific action.
- Executed and Executory Contracts: An executed contract is fully performed, whereas an executory contract still has obligations to be fulfilled.
Legal Implications of Breaching a Contract When one party fails to fulfill their contractual obligations, a breach occurs. The consequences of a breach depend on its severity and impact. Legal remedies for breach of contract include:
- Damages: The non-breaching party may receive monetary compensation for losses suffered due to the breach.
- Specific Performance: A court may order the breaching party to fulfill their contractual obligations.
- Rescission: The contract may be canceled, and both parties restored to their original positions before entering the agreement.
- Restitution: The breaching party may be required to return any benefit unjustly received.
Best Practices for Drafting and Enforcing Contracts To minimize the risk of disputes and breaches, parties should adhere to best practices when drafting and enforcing contracts:
- Clearly Define Terms: Ensure all contract terms are precise, leaving no room for misinterpretation.
- Put Agreements in Writing: While verbal contracts can be legally binding, written agreements provide stronger evidence and clarity.
- Include Dispute Resolution Clauses: Outline mechanisms such as mediation or arbitration to resolve disputes efficiently.
- Review and Update Contracts: Regularly review contracts to ensure they remain relevant and compliant with legal changes.
- Seek Legal Advice: Consult a lawyer to draft or review contracts to avoid legal pitfalls.
Conclusion Understanding contract law is crucial for individuals and businesses to safeguard their rights and obligations. By ensuring contracts meet legal requirements and incorporating best practices, parties can prevent disputes and protect their interests. In case of breaches, legal remedies provide avenues for enforcement and compensation. Staying informed about contract law enables parties to navigate agreements effectively and uphold legal responsibilities.